 |
 |
- Search
| J. Conserv. Sci > Volume 38(4); 2022 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Built in the 6th and 7th centuries during the Baekje period, the Buyeo Royal Tombs consist of seven tombs, including Tomb No. 1, which contains murals. To preserve Tomb No. 1 from damage caused by microorganisms, periodic microbial-distribution investigations are conducted. Following such investigations in August 2016, June 2018, and November 2019, the microbes were classified according to the investigation period, location of collection, and space. This study compares and analyzes the results. The concentration of airborne microorganisms in Tomb No. 1 and the number of microbial genera identified in each space of the tomb decreased as proximity to the main room with murals diminished. During the investigation period, the genera Bacillus, Cladosporium, Penicillium, and Streptomyces were commonly identified on Tomb No. 1. The microorganisms collected f rom the main room walls were mostly isolated from the east and west walls where the genera Bacillus, Cupriavidus, Paenibacillus, Pseudomonas, and Streptomyces were commonly identified in three or more walls. In particular, the genus Streptomyces is a dangerous strain capable of damaging murals by penetrating into and discoloring the pigments on them. The data generated from this study may be useful for future research on microbial distribution in other domestic mural tombs and those located in North Korea and abroad.
Ancient tombs, monuments in which human corpses were buried, provide historical and archaeological data. Mounded tombs were constructed by covering the upper part of the burial with soil or stone (Park, 2006). In the Republic of Korea, ancient tombs are generally attributed to the Three Kingdoms period (Beack, 2017). Various burial relics and murals can be found inside ancient tombs. Tomb murals are evaluated as materials of rich historical and cultural value because they provide some insight into the lifestyles, customs, and religious views of ancient societies.
Ten mural tombs exist in the Republic of Korea. The Yeongju Sunheung Mural Tomb, Yeongju Sunheung Eo Suk Tomb, Gongju Royal Tomb No. 6, Goryeong Goari Mural Tomb, and Buyeo Royal Tomb No. 1 were built during the Gaya and Three Kingdoms period (National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage, 2019). For this study, the Buyeo Royal Tomb No. 1 (hereafter referred to as Tomb No. 1) was selected as the research site among the mural tombs of the Three Kingdoms period in Korea (Figure 1A-B). Tomb No. 1 is an ancient tomb that belongs to the Royal Tombs of Buyeo (late 6th to early 7th centuries), which consist of seven tombs. The Royal Tombs of Buyeo, designated as Historic Site No. 14 in 1963, were simultaneously included in the Baekje World Historic Area and registered as a UNESCO World Heritage site in 2015. Among the seven tombs, Tomb No. 1 is the only tomb with murals painted on the four walls and ceiling of the tomb chamber. The four guardian deities are painted on the east, west, south, and north walls of the main room, and lotus and cloud patterns are engraved on the ceiling.
Tomb No. 1 was the first tomb to be investigated during the Japanese colonial period from 1915 to 1917 (Buyeogun, 2008). At the time of that initial investigation, the murals were relatively clear, but they are are now largely faded (Lee, 2000; National Research Foundation of Korea, 2021). A systematic and comprehensive investigation of Tomb No. 1 began in 2008, and the murals’ condition, cause of damage, and preservation environment were first examined. The current study focuses on the microbial distribution within the tomb; thus, relevant findings from previous research will first be presented.
A 2008 study by Gyeongju University focused on identifying fungi, bacteria, green algae, and cyanobacteria by collecting microorganisms from locations where discoloration had occurred because of living organisms (Buyeogun, 2008). In 2013, the airborne and wall microbial distribution inside and outside of Tomb No. 1 was confirmed, and a report predicting the growth of microbes, which may damage the murals, was created based on the general microorganism growth-temperature (Buyeogun, 2013). Subsequent monitoring of microbial distribution was conducted in 2016, using the same methodology as in the 2013 study (Buyeogun and Backje World Heritage Center, 2016). In 2018, microbial research attempted to analyze substances presumed to be microorganisms generated on the wall of main room along with their distribution status (Buyeogun and Backje World Heritage Center, 2018). Research projects to identify the suspected microorganisms found inside Tomb No. 1 have been undertaken twice (National Research Foundation of Korea, 2019; 2020).
The above research is significant because it can help predict a mural’s risk of damage based on the microbial distribution in Tomb No. 1. However, the status of the microbial distribution can only be measured at a specific point of time. In the current study, the microbial distribution statuses of Tomb No. 1, collected in 2016, 2018, and 2019, were classified according to the investigation period, location of collection, and the space it occupied. Subsequently, the results were compared and analyzed.
The interior of Tomb No. 1 comprises four spaces: the entrance, aisle, front room, and main room with murals, the size of which may be found in Figure 2. In our study, throughout the four-year period, we conducted our research in accordance with the monitoring cycle of Tomb No. 1 and the 2013 report titled “Microorganism Occurrence Risk Prediction”. Airborne microorganisms existing within and outside of each space were investigated in August 2016, June 2018, and November 2019 (Figure 2). Microorganisms were collected for two minutes at a flow rate of 100 L/min a fter the potato dextrose agar (PDA, Difco, USA) medium was mounted on a biological sampler (BUCK Bio-CultureTM, B30120 Pump, A.P. Buck, Inc., USA). The collection was repeated 2‒3 times in each space, and the microorganisms were cultured in an incubator (WIG-155, DAIHAN Scientific, KOR) at 30±2℃ and a relative humidity of 50±5%.
The microorganisms on the wall of Tomb No. 1’s main room were collected simultaneously with airborne microorganisms. They were collected from the center, which was determined after dividing each wall at regular intervals. Microorganisms were collected from several collection sites ―24 points from the East wall, 24 points from the West wall, 10 points from the South wall, 12 points from the North wall, and 18 points from the ceiling―using sterile swabs (Figure 2). The collected microorganisms were placed on a PDA medium and then cultured in an incubator for about two to five days.
The number of microbial colonies was counted with the naked eye or using a colony counter (CC-1, AS-ONE, JPN), and the concentration was confirmed by calculating the number of colonies per unit volume in the air (colony forming units [CFU/m3]).
Cultured microorganisms were isolated into a single colony based on the colony’s form, size, and color. Fungi were cultured in the PDA medium, and bacteria were cultured in nutrient agar (NA, Difco, USA) after inoculation. This process was performed until a single colony of microorganisms was isolated. After undergoing one more morphological classification, sequencing analysis was performed.
For sequencing, the identification service of Macrogen (Seoul, KOR) was used. Fungi were primarily analyzed with the sequencing of the 26S rRNA gene (D1/D2/D3 region), and the ITS region and 18S rRNA region were secondarily analyzed for the unidentified strain. Bacteria were analyzed with a 16S rRNA region. The analyzed sequencing was identified by using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
During our investigations in August 2016, June 2018, and November 2019, the average number of microorganisms collected from inside and outside of Tomb No. 1 was as follows: 34 from the outside, 106 at the entrance, 59 in the aisle, 45 in the front room, and 12 in the main room (Table 1). The number of microorganisms tended to decrease from the outside to inside, with the entrance having the highest concentration.
The concentration of microorganisms in August 2016 and November 2019 was “too numerous to count” (TNTC) in the entrance, aisle, and front room. The concentration of microorganisms in the main room was the lowest at 243 CFU/m3 and 6 CFU/m3 in 2016 and 2019, respectively. The concentration of microorganisms in June 2018 was TNTC outside and at the entrance of Tomb No. 1, while it was confirmed that the average concentration of microorganisms was 305 CFU/m3 for the aisle and front room, and 144 CFU/m3 for the main room (Table 1).
Twenty genera and 40 species were identified from the microorganisms collected in August 2016. Among the microorganisms, 14 fungi genera (such as Aspergillus) and six bacteria genera (such as Arthrobacter) were identified. The genera Penicillium and Bacillus were the dominant microbes, which accounted for a high distribution rate of 15.0% and 12.5%, respectively (Figure 3A). In June 2018, 21 species from 18 genera (11 fungal genera, seven bacterial genera) of microorganisms were isolated, and no dominant microbe was identified as the microorganisms were composed of one or two strains and belonged to each genus unit (Figure 3B). In November 2019, 35 species from 24 genera of microorganisms were identified. Among them, 16 genera of fungi and eight genera of bacteria were identified. The genus Aspergillus, which occupies a high distribution rate of 14.3%, was identified as the dominant microbes (Figure 3C).
During the entire investigation, the genera Bacillus, Cladosporium, Penicillium, and Streptomyces were commonly isolated (Figure 3A-C). Bacillus genus is a representative soil microorganism, and a total of seven species (B. cereus, B. flexus, B. megaterium, B. pseudomycoides, B. safensis, B. stratosphericus, and B. thuringiensis) were identified. Cladosporium genus was identified with C. cladosporioides, C. halotolerans, C. tenuissimum, and C. sp.; C. sp. grows optimally at 18∼28°C, and can also grow at 30∼35°C (Larone, 1987; Patterson and McGinnis, 2009). Penicillium genus was identified with P. copticola and six other species (P. decumbens, P. herquei, P. oxalicum, P. rolfsii, P. sanguifluum, and P. sp.) and Streptomyces genus, a type of actinomycetes, was identified with five species (S. durhamensis, S. galbus, S. naganishii, S. nojiriensis, and S. subrutilus). Data on microbial species in this content are not presented in tables or graphs.
In August 2016, genera collected in each space comprised the following: eight genera of microorganisms from the outside, 12 genera at the entrance, five genera in the aisle, 11 genera in the front room, and eight genera in the main room. Moreover, all microorganisms were also found inside except for the genus Nigrospora, which was collected from the outside. The genera Aspergillus and Penicillium were isolated from all interior spaces, whereas Leptosphaerulina and Paraconiothyrium were identified only in the main room with the murals. In June 2018, Alternaria and six other genera (Cladosporium, Mucor, Pantoea, Paraphaeosphaeria, Phoma, and Subsessila) were collected from the outside (Table 2). Among them, the genera Alternaria, Cladosporium, and Paraphaeosphaeria were also found. As we entered the interior space, the number of collected microorganisms decreased; Arthrobacter and Tsukamurella were found only in the main room. In November 2019, a total of nine genera of microorganisms were identified outside; among them, genera Bacillus, Cladosporium, Phaeosphaeriacea, and Robillarda were also found inside. Specifically, Aspergillus was identified in all interior spaces, whereas Bacillus and Cladosporium were isolated from the entrance, aisle, and front room. Achromobacter and 15 other genera were only collected during this investigation (Table 2).
The microorganisms collected in August 2016 were classified into 32 genera and 50 species. The microbial genus unit included 14 fungal genera (such as Bionectria) and 18 bacterial genera (such as Acinetobacter). Streptomyces (10.0%), Mortierella (8.0%), and Paenibacillus (8.0%) were identified as the dominant microbes (Figure 3D). In August 2018, 41 genera and 68 species of microorganisms were classified, and a total of 21 fungal genera and 19 bacterial genera were identified. Streptomyces (14.7%), Bacillus (8.8%), and Paenibacillus (7.4%) were identified as the dominant microbes (Figure 3E), with the genus Streptomyces occupying the highest distribution ratio and identified with S. atratus and nine other species (data not shown). In November 2019, 36 genera (20 fungal genera, 16 bacterial genera) and 77 species of microorganisms were classified; the genus Streptomyces was identified as the dominant microbe with a distribution ratio of approximately 5% or more (Figure 3F).
During the investigation, B. cereus and eight other species (C. basilensis, C. campinensis, D. japonica, F. oxysporum, M. sp., P. alginolyticus, P. terrae, and V. boronicumulans) were identified. C. basilensis and C. campinensis are Gram-negative bacteria isolated from the soil (Goris et al., 2001), and the optimum growth temperature was reported to be 25∼30℃ (CCUG 49340; DSM 11853). D. japonica is a gram-negative bacterium mainly found in soil. This strain can flourish at 10∼37℃, grows optimally at a temperature of 25∼30℃ and pH 5.6∼8.0 (Xie and Yokota, 2005), and produces a bright orange pigment (Dar et al., 2020). V. boronicumulans has a yellow color, and optimum growth conditions require a temperature of 4∼37℃ and a pH of 5∼ 9 (Miwa et al., 2008). Data on microbial species in this content are not presented in tables or graphs.
In August 2016, June 2018, and November 2019, the average number of microbial genera isolated from the main room wall was calculated. Most microorganisms were found on the East wall (20 genera), followed by the West wall (18 genera), the South and North walls (14 genera each), and the ceiling (13 genera).
In August 2016, Bacillus and eight other genera were identified on three or more walls; genera Cupriavidus and Mortierella were found isolated on all the walls. In June 2018, the east and west walls isolated 20 genera, the most significant number of microorganisms. The genera Bacillus, Cupriavidus, and Streptomyces were isolated from all walls, whereas six species from the genus Bacillus, three species from the genus Cupriavidus, and 10 species from the genus Streptomyces were identified. In November 2019, Bacillus and 14 other genera were isolated from three or more walls, including Bacillus, Chaetomium, Cupriavidus, Mortierella, Pseudomonas, and Streptomyces which were isolated from all walls (Table 3). Among microorganisms, the genus Streptomyces was identified the most, with a total of 14 species (Data not shown).
During the entire investigation period, Bacillus, Cupriavidus, Paenibacillus, Pseudomonas, and Streptomyces were commonly identified on three or more walls (Table 3). The genus Bacillus is an aerobic and facultative anaerobic strain commonly present in soil and nature (Cohn, 1872). Among the genus Bacillus, B. cereus was identified in all investigation periods and is known to grow at 10∼50℃ (ICMSF, 1996). The genus Cupriavidus is a strain commonly found in soil, and in August 2016 and June 2018, C. basilensis was isolated from all walls. C. basilensis grows optimally at 25∼30℃ (CCUG 49340; DSM 11853), and it has been confirmed in soil samples taken from burial relics inside the ancient tombs (Ha et al., 2013). In November 2019, C. campinensis, C. necator, and C. numazuensis were identified on all the walls. The genus Paenibacillus exists in a variety of environments such as soil, water, and plants (McSpadden Gardener, 2004; Montes et al., 2004; Ouyang et al., 2008; Padda et al., 2017), and P. alginolyticus and seven other species were isolated. The genus Streptomyces is a kind of actinomycetes and it mainly inhabits decaying plants and soil. S. alboniger and 20 other s train species were identified on the walls, and among them, S. aureus, S. cirratus, S. lavendulae, S. subrutilus, and S. xanthophaeus were most isolated. Data on microbial species in this content are not presented in tables or graphs.
In this study, the microbial distribution statuses of Tomb No. 1 in August 2016, June 2018, and November 2019 were compared and analyzed according to the investigation period, location of collection, and space.
The results reveal that the concentration of airborne microorganisms inside Tomb No. 1 decreased as one got closer to the main room. The number and concentration of microorganisms in the entrances adjacent to the outside were highest in all investigation periods. This is believed to be caused by the increase in microbial contamination due to the habitat of insects belonging to the family Rhaphidophoridae. Another major reason for this phenomenon may be the presence of stagnant air over a long period in the outer space that is let into the tomb when someone enters or leaves. Therefore, installing ultraviolet light for sterilization or using an air sterilizer to control microorganisms is required.
The concentration of airborne microorganisms in the main room with murals was in the range of 6‒243 CFU/m3. Currently, it is difficult to estimate the level of risk posed to the murals in terms of potential damage that they may suffer due to the lack of standards regarding the concentration of airborne microorganisms in the ancient tombs or a conservation and management plan regarding the same domestically or internationally. However, we have confirmed that the levels present in the tomb are lower than those stipulated by the maintenance and recommendation standards of the Enforcement Regulations of the Indoor Air Quality Management Act (total airborne bacteria 800 CFU/m3 or less, fungi 500 CFU/m3 or less).
The genera Aspergillus, Bacillus, Cladosporium, Penicillium, and Streptomyces were mostly distributed in Tomb No. 1, and the distribution of dominant microbes collected in August 2016 and November 2019 were similar. According to the “Microbial Occurrence Risk Prediction of Buyeo Royal Tomb No. 1”, the period from March to July was estimated to be the “safe period for microbial occurrence,” while August‒ February of the following year was estimated to be the “caution period for microbial occurrence” (Buyeogun, 2013). It can be inferred that the microbial distribution was similar because the two investigation periods belonged to the “caution period for microbial occurrence.” Microorganisms collected i n June 2 0 18 b elonged to t he “ safe p eriod for microbial occurrence” as only a relatively small number of microorganisms were isolated compared with August 2016 and November 2019. Moreover, the genus Arthrinium and nine other genera were confirmed only during this period.
A difference in the microbial distribution in each space inside Tomb No. 1 was also discovered. Some factors such as temperature, humidity, and nutrient sources affect microbial growth (Garg et al., 1995; Seo et al., 2013); thus, it can be inferred that the microbial distribution in Tomb No. 1 was different due to differences in external air inflow and temperature. Aspergillus, Bacillus, Cladosporium, and Penicillium detected from the outside were found in the front and main room and are thought to have been introduced by the air flowing in from outside. The average temperature of each interior space according to the investigation period was 16.2°C in August 2016 (aisle: 16.9°C, front room: 16.2°C, main room: 15.5°C), 13.7°C in June 2018 (aisle: 14.0°C, front room: 14.1°C, main room: 13.0°C), and 18.2°C in November 2019 (aisle: 18.1°C, front room: 18.4°C, main room: 18.1°C) (Buyeogun and Baekje World Heritage Center, 2016; 2018; National Research Foundation of Korea, 2019). It is assumed that the microbial distribution varied because the temperature difference occurred from a minimum of 0.3°C to a maximum of 5.4°C according to the time and space of microbial investigation.
In the case of wall microorganisms, the genus Streptomyces occupied a high average distribution ratio of 14.2% in all investigation periods and was identified as the dominant microbe. Most strains of the genus Streptomyces have the characteristic of producing and secreting a protective pigment in the absence of excess salt, biocide, ultraviolet rays, and nutrients (Korea Dictionary Research Publishing, 1996; Sakr et al., 2012). In addition, as it has been reported that various metabolites secreted by most Streptomyces strains can discolor pigments (Abdel-Haliem et al., 2013), they comprise risk strains that can damage murals. Similar species were isolated from Gongju Royal Tomb No. 6, Korea (Gongju City and KNU-Research Institute for Basic Science, 2020), and identified in ancient Egyptian tombs, the Altamira Caves in Spain, and the Kitora and Takamatsuzuka tombs in Japan (Abdel-Haliem et al., 2013; Portillo et al., 2008; Sakr et al., 2012).
Until now, the microbial distribution in Buyeo Royal Tomb No. 1 has been periodically monitored. However, the results are limited to a specific period of time. This research is significant because it comparatively analyzed the microbial distribution in Tomb No. 1 according to investigation period, location of collection, and space, and identified the growth characteristics of microorganisms specific to Tomb No. 1 and dangerous strains that could damage the murals. The data generated from this study can be compared with those generated from future research on microbial distribution in mural tombs located domestically, in North Korea, and abroad.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was conducted with support from Buyeogun and the Baekje World Heritage Center as part of the research “Monitoring conservation environment of the Ancient Tombs in Neungsan-ri” and “Continuous monitoring Donghachong of the Ancient Tombs in Neungsan-ri’’ conducted in 2016 and 2018, respectively.
This research was supported by the International Research & Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Grant number: 2019K1A3A1A25000303).
Figure 1.
Location of Tomb No. 1 in Neungsan-ri, Buyeo. (A) Aerial photograph of Tomb No. 1 (photo source: Baekje World Heritage Center), (B) Front view of Tomb No. 1.
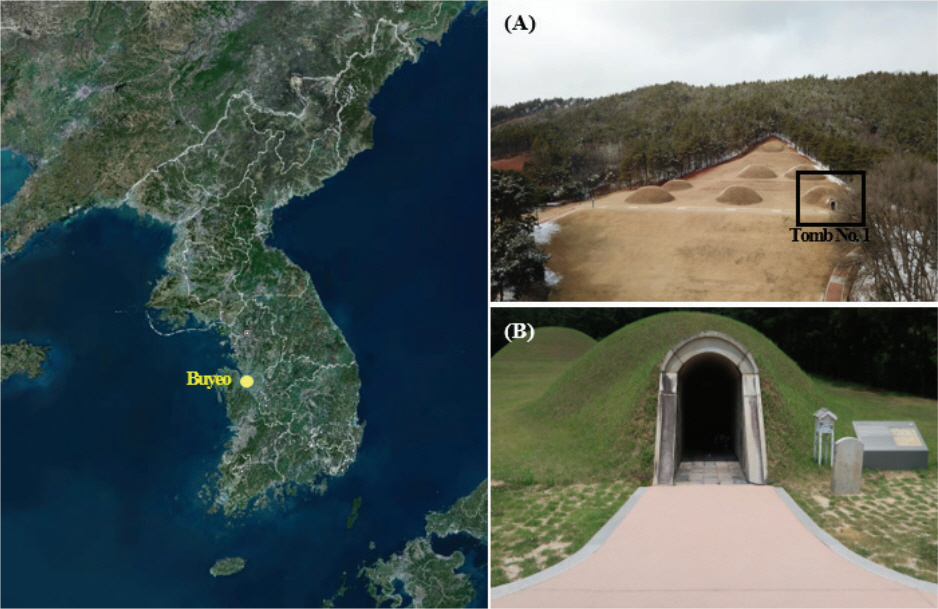

Figure 2.
The locations from which airborne and wall microorganisms in Tomb No.1 were collected (Buyeogun and Baekje World Heritage Center, 2016; 2018; Buyeogun, 2017; National Research Foundation of Korea, 2019).
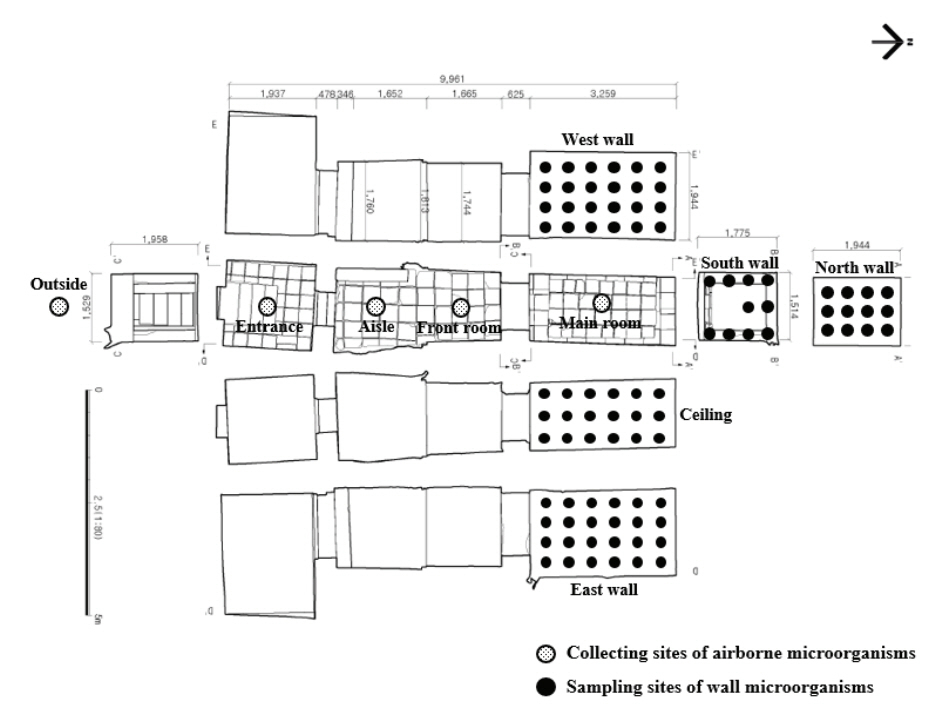
Figure 3.
Airborne and wall microbial distribution in Tomb No. 1 classified by investigation periods.
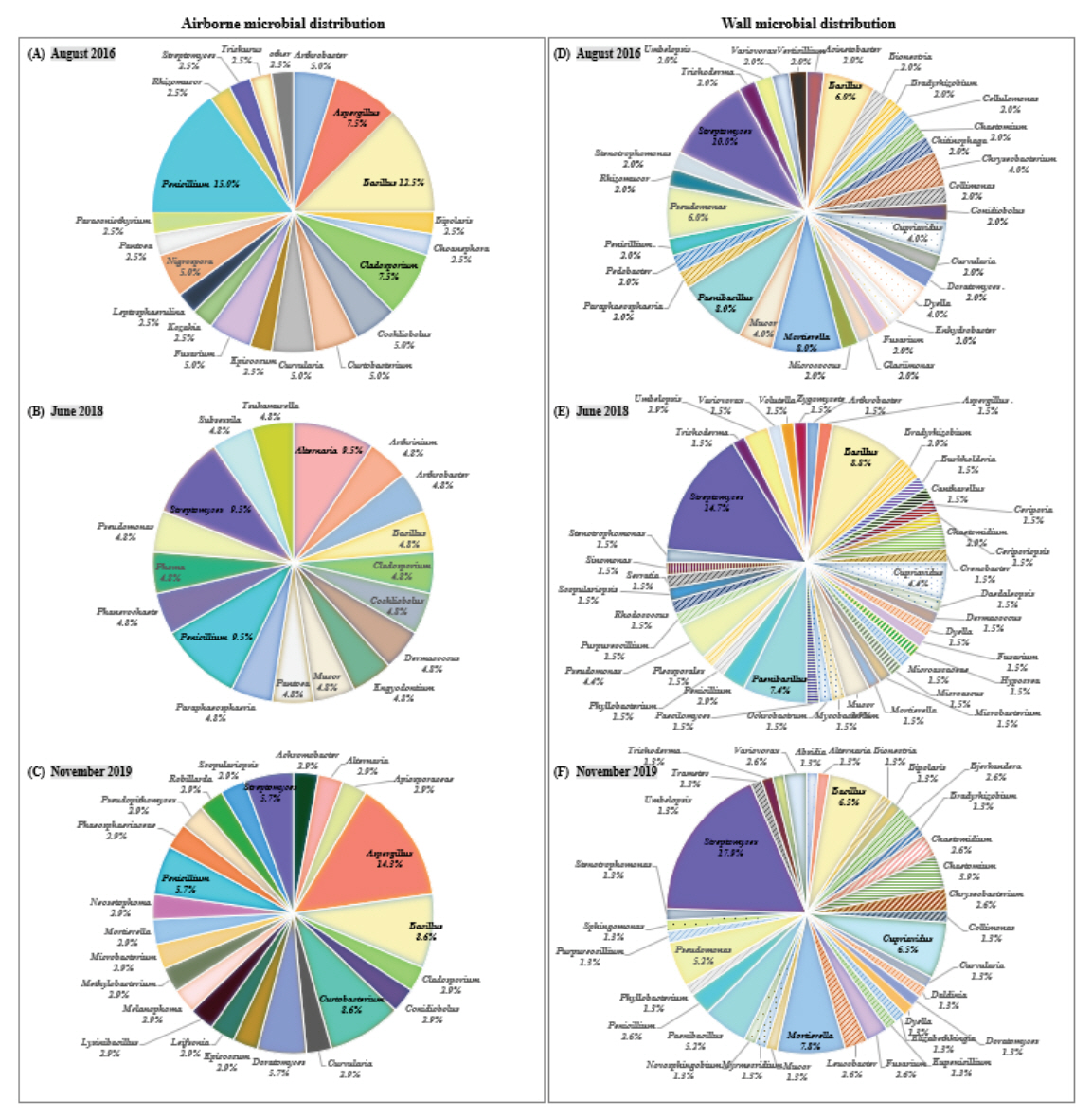
Table 1.
The numbers and concentration of airborne microorganisms inside and outside of Tomb No. 1
Table 2.
Distribution of airborne microorganisms based on the space of Tomb No. 1 where they were found
Table 3.
Distribution of surface microorganisms by wall sites in Tomb No. 1’s main room
REFERENCES
Abdel-Haliem, M.E.F., Sakr, A.A., Ali, M.F., Ghaly, M.F. and Sohlenkamp, C., 2013, Characterization of Streptomyces isolates causing colour changes of mural paintings in ancient Egyptian tombs. Microbiological Research, 168(7), 428–437.


Baeck, S.O., 2017, The historical interpretation of ancient royal tombs in Gaya(加耶). The Journal of Korean Ancient History, 88(88), 133–164.

Buyeogun, Backje World Heritage Center, 2016, Monitoring the conservation environment of the Ancient Tombs in Neungsan-ri, 139.
Buyeogun, Backje World Heritage Center, 2018, Continuous monitoring of Donghachong of the Ancient Tombs in Neungsan-ri, 171.
Buyeogun, 2008, Investigation of the conservation environment of the Ancient Tomb Donghachong in Neungsan-ri, Buyeo, 334.
Buyeogun, 2013, Environmental monitoring of the Ancient Tomb Donghachong in Neungsan-ri, Buyeo, 38.
Buyeogun, 2017, Analysis of the conservation environment of Donghachong in Neungsan-ri, Buyeo, Recoroding project of survey on Ancient Tombs in Neungsan-ri, Buyeo, 202.
Cohn, F., 1872, Untersuchungen über Bakterien. Beitrage zur Biologie der Pflanzen. 1 Heft 2, 127–224.
Dar, D., Thomashow, L.S., Weller, D.M. and Newman, D.K., 2020, Global landscape of phenazine biosynthesis and biodegradation reveals species-specific colonization patterns in agricultural soils and crop microbiomes, Elife, 9.
CCUG; Culture Collection University of Gothenburg, “Cupriavidus basilensis CCUG 49340”, https://www.ccug.se/
DSM 11853, Leibniz Institut DSMZ-Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH, “Cupriavidus basilensis DSM 11853”, https://www.dsmz.de/
Garg, K.L., Jain, K.K. and Mishra, A.K., 1995, Role of fungi in the deterioration of wall paintings. Science of the Total Environment, 167(1-3), 255–271.

Gongju City, Kongju National University-Research Institute for Basic Science, 2020, Research on the internal monitoring and analysis of the Ancient Tombs in Songsan-ri, Gonju, 258.
Goris, J., De Vos, P., Coenye, T., Hoste, B., Janssens, D., Brim, H., Diels, L., Mergeay, M., Kersters, K. and Vandamme, P., 2001, Classification of metal-resistant bacteria from industrial biotopes as Ralstonia campinensis sp. nov., Ralstonia metallidurans sp. nov. and Ralstonia basilensis Steinle et al. 1998 emend. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 51(5), 1773–1782.


ICMSF; International Commission on Microbiological Specifications for Foods, 1996, Microorganism in Foods 5 -Characteristics of Microbial Pathogens-, Springer, US.
Korean Dictionary Research Publishing, 1996, The great encyclopedia of nursing science, Korean Dictionary Research History Editorial Department.
Larone, D.H., 1987, Medically important fungi: a guide to identification, Elsevier, New York, 196, 203.
Lee, N.S., 2000, The Ancient Tombs in Neungsan-ri and Backje royal tombs. The Research Institute of Backje Culture, 29(29), 1–24.
McSpadden Gardener, B.B., 2004, Ecology of Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp. in agricultural systems, Phytopathology. The Research Institute of Backje Culture, 94(11), 1252–1258.
Miwa, H., Ahmed, I., Yoon, J., Yokota, A. and Fujiwara, T., Variovorax boronicumulans sp. nov., a boron-accumulating bacterium isolated from soil. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 58(1), 286–289.


Montes, M.J., Mercadé, E., Bozal, N. and Guinea, J., 2004, Paenibacillus antarcticus sp. nov., a novel psychrotolerant organism from the Antarctic environment”. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54(5), 1521–1526.


National Research Foundation of Korea, 2019, Research of conservation environment and eco-friendly damage control of cultural heritage Korea and Italy, 83.
National Research Foundation of Korea, 2020, Research of conservation environment and eco-friendly damage control of cultural heritage Korea and Italy, 57.
National Research Foundation of Korea, 2021, Research of conservation environment and eco-friendly damage control of cultural heritage Korea and Italy, 63.
National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage, 2019, The tomb murals in South Korea, 329.
Ouyang, J., Pei, Z., Lutwick, L., Dalal, S., Yang, L., Cassai, N., Sandhu, K., Hanna, B., Wieczorek, R.L., Bluth, M. and Pincus, M.R., 2008, Paenibacillus thiaminolyticus: a new cause of human infection, inducing bacteremia in a patient on hemodialysis. Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, 38(4), 393–400.
Padda, K.P., Puri, A. and Chanway, C.P., 2017, Paenibacillus polymyxa: a prominent biofertilizer and biocontrol agent for sustainable agriculture, In: Agriculturally important microbes for sustainable agriculture, Springer, Singapore, 165–191.
Park, M.J., 2006, Excavation methods for the mound tombs of the Three Kingdoms period. The Journal of Korean Field Archaeology, 1(1), 147–174.
Patterson, T.F. and McGinnis, M.R., 2009, The fungi: description. Site Doctor Fungus, Mycoses Study Group.
Portillo, M.D.C., Gonzalez, J.M. and Saiz‐Jimenez, C., 2008, Metabolically active microbial communities of yellow and grey colonizations on the walls of Altamira Cave, Spain. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 104(3), 681–691.


Sakr, A.A., Ali, M.F., Ghaly, M.F. and Abdel-Haliem, M.E.F., 2012, Discoloration of ancient Egyptian mural paintings by Streptomyces strains and methods of its removal. International Journal of Conservation Science, 3(4), 249–258.
Seo, M.S., Lee, S.M. and Hong, J.Y., 2013, The characteristic study of the microbial habitat in the Muwisa Museum, Gangjin. Journal of Conservation Science, 29(4), 333–343.

- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- 1,660 View
- 51 Download
-
Related articles in
J. Conserv. Sci.